Price
The price is what is paid, generally money, in an exchange to acquire a good or service. 4 21 48
The price has an influence on the quantity that is feasible to sell, and therefore on the performance of the project.
The price according to the market structure
In perfect competition
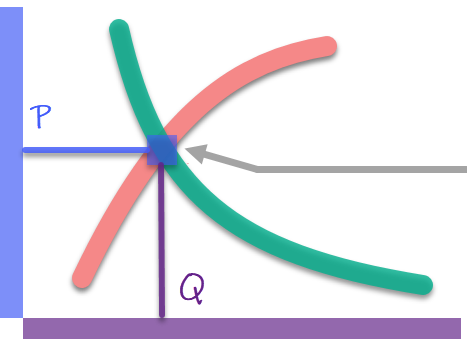
Remember that demand and supply are independent.
In perfect competition there are many undifferentiated suppliers, and the equilibrium price is obtained when the quantity and price at which the suppliers are willing to sell are equal to the quantity and price at which the buyers are willing to buy .
The bidders are price acceptors , if a company raises the price it will not sell, because they will go with any other bidder, if it lowers it it will sell, but there is no case because it could sell more expensively, nobody has control over the price, it is defined by "the market ".
|
|
Demand |
Supply |
|
|
Price |
|
Equilibrium price |
|
|
|
Quantity |
|
|
In monopoly
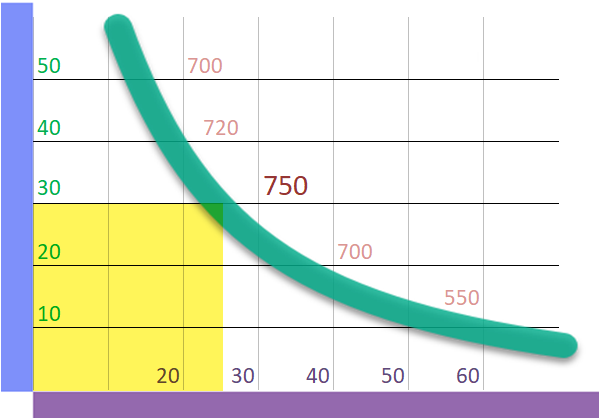
There is demand, but there is no 'supply curve' because the monopoly is the only supplier, therefore, it can give whatever price it considers convenient. Income is given by multiplying the price x the quantity demanded, and the price that the monopoly will decide will be, in general, the one that allows it the highest income. This model is called a "single price monopoly."
Let's put some numbers on the graph, where 'sales = price x quantity' .
|
|
Demand |
|
|
Price USD per piece |
|
In this example: The maximum value is reached at $ 30 x 25 = 750, The price that maximizes the sale is $ 30 USD |
|
|
Quantity, thousands of pieces |
|
The monopoly can sell at the price that maximizes its income, but in addition, it can customize products and prices to offer them to different groups, further increasing its income.
Perfect competition and monopoly are extreme cases , it is useful to know how each one determines the price because the real market structure of your project is between these two, especially if you have a differentiator that allows you to be in monopolistic competition, you will have some elements of control over price.
Decide on your Base Price, which is the general price level at which the company expects to sell the product.
How to determine the price.
1. Decide on the strategy
The overall strategy is the basic long-term pricing structure , which includes the initial price of a product and the intended direction for price movements during the product's life cycle. There are three basic strategies:
- Price of ´Status Quo´
In general it is to adjust to the prices of competitors, substitutes, or alternatives . It is the most common and is a safe long-term strategy, especially for small and medium-sized companies. Most products or services, even if they are novel, are introduced to the market at a price similar to that of their alternatives. If in doubt, choose this strategy.
Electronic books have minimal manufacturing and distribution costs compared to physical books, they are cheaper, but only 26%, and it is likely that over time the differential will be greater, but not because electronic books decrease, but because they will increase on paper . PayPal has a transaction price of between 4 and 5%, similar to the cost of processing payments with Credit Cards which is between 2 and 6%, competing for its differentiators such as ease of use and guarantees. Uber has the 'dynamic rate' that explicitly takes advantage of temporary increases in demand or reduction in supply to adjust the price in real time in the geographical area where it operates .. 46
A "tracker" or "Beacon" is a device that tracks critical variables in products such as food, medicine, or industrial products, for example for the 'cold chain', these devices are "new", there is no price reference Historical records, then, to determine the initial price, one can start from the losses caused by the lack of control in the cold chain and from there raise a benefit for the user . Although there are no competitor prices, the impact can be calculated, it is also a status quo strategy 102
- Price skimming
Starts with a high introductory price to recoup development costs, tapering over time to encompass a larger market. Frequent in technological products, new, or protected with patents or with other strong barriers to entry, such as medicines, cell phones, hardware, video games, or automotive technology. The skimming process can take years or decades.
The ABS anti-lock braking system was invented in 1978 only for airplanes and luxury cars because of its high price, at that time only specialists were convinced of its usefulness (innovators) in 1989 it was only included in 0.6% of vehicles. Now people know and request it, 75% of cars already include it (it is in the late majority stage) and in Europe it is mandatory, the volume of sales allows the system to have more accessible prices (750 USD) . 44
- Penetration Pricing
When a company starts with a low price to reach a mass market that will benefit from an indirect price model, for example with advertising. This strategy is useful for products that people 'already wait' in price-sensitive markets.
Applications (App) for cell phones or tablets, such as games, art, communication, shopping, productivity, or that use GPS are distributed at prices that can be from $ 0 USD because they receive their income from advertising, sales in the application, or versions Pro. 45
Important: this strategy is not to compete on low price , since it also seeks to maximize revenue using complementary models, such as advertising, sale of accessories, data analysis, and others.
2. Use tactics to fine-tune the price.
They are short-term approaches that temporarily change the base price to adjust to competition in certain markets, satisfy legislation, or take advantage of unique supply or demand situations, or other opportunities.
Offering different models, versions, or complements, temporary discounts, using psychological prices (like $ 99.90), dividing the product into parts, or adding services are tactics to refine the price.
Sheet
Comparison of prices with respect to competitors.
Example
LoggGuitars company produces a 3-string guitar, especially for children to learn to play easily. It is a well differentiated, innovative, creative product, with excellent design, and has its own method of musical teaching. These are your direct competitors and their prices 52

Logg Pro Acustic. Competitors and prices
|
Producto |
Empresa |
Precio USD |
Características |
|
Logg Pro Acustic 8+ |
Logg Guitarr |
159 |
Design, own method |
|
Acoustic Guitar 1/4 |
Gibson |
190 |
Prestige, variety |
|
Acoustic Guitar 1/4 |
Fender |
160 |
Prestige, sound |
|
Economic models |
100 marcas |
80-120 |
Low price |
|
Skier Stratocaster Electric |
Skier |
250 |
Own method, distribution |
|
|
|
|
|
Processor
1. General pricing strategy.
Direct competitors are 6-string classical acoustic guitars, with 1/4 being the ones suitable for children, with prices ranging from $ 60 to $ 160 USD, the most expensive are from the Gibson brand, very well positioned, which go up to $ 190 USD (see table above). The entrepreneur chose a " Status Quo " price since it does not go outside of that range ... let's say it will be $ 150 to $ 180 USD.
2. Tactics to fine-tune the price
Use psychological prices, different models, and sale of accessories to increase the purchase per customer. Although the guitar costs $ 159 USD, if we add the tuner, the bag, the strap, and a couple of spare strings, the bill goes up to $ 290 USD ... and there will be someone who will also take the amplifier, the book collection, and a couple of t-shirts.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Market Study |
|
|
|
Chapter 1.4. Price Logg Pro Acustic. |
|
|
|
General strategy Competitors are 1/4 guitars, priced from $ 60 to $ 160 USD, Gibsons going up to $ 190 USD. Logg Pro Acustic base price: $ 159 USD. Refine the base price: 1. Electric $ 199 USD (+ 25%), Special edition $ 299 USD.. 2. Accessories: Booth. 39 USD Tuner. $ 19 USD Amplifier. 49 USD Bag 29 USD Others: books, strings, t-shirts, gift cards. 3. Discount policy 10-50, -15% 50+, -20% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
More information on the web.
Creado con el Personal Edition de HelpNDoc: Producir ayuda online para aplicaciones Qt